name: inverse layout: true class: center, middle, inverse <div class="my-header"><span> <a href="/training-material/topics/epigenetics" title="Return to topic page" ><i class="fa fa-level-up" aria-hidden="true"></i></a> <a class="nav-link" href="https://github.com/galaxyproject/training-material/edit/main/topics/epigenetics/tutorials/formation_of_super-structures_on_xi/slides.html"><i class="fa fa-pencil" aria-hidden="true"></i></a> </span></div> <div class="my-footer"><span> <img src="/training-material/assets/images/GTN-60px.png" alt="Galaxy Training Network" style="height: 40px;"/> </span></div> --- <img src="/training-material/assets/images/GTN.png" alt="Galaxy Training Network" class="cover-logo"/> # ChIP-seq data analysis <div markdown="0"> <div class="contributors-line"> Authors: <a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/LeilyR/" class="contributor-badge contributor-LeilyR"><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/LeilyR?s=27" alt="Avatar">Leily Rabbani</a> <a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/bebatut/" class="contributor-badge contributor-bebatut"><img src="/training-material/assets/images/orcid.png" alt="orcid logo"/><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/bebatut?s=27" alt="Avatar">Bérénice Batut</a> </div> </div> <!-- modified date --> <div class="footnote" style="bottom: 8em;"><i class="far fa-calendar" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="visually-hidden">last_modification</span> Updated: Jul 26, 2021</div> <!-- other slide formats (video and plain-text) --> <div class="footnote" style="bottom: 6em;"> <i class="fas fa-file-alt" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="visually-hidden">text-document</span><a href="slides-plain.html"> Plain-text slides</a> </div> <!-- usage tips --> <div class="footnote" style="bottom: 2em;"> <strong>Tip: </strong>press <kbd>P</kbd> to view the presenter notes | <i class="fa fa-arrows" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="visually-hidden">arrow-keys</span> Use arrow keys to move between slides </div> ??? Presenter notes contain extra information which might be useful if you intend to use these slides for teaching. Press `P` again to switch presenter notes off Press `C` to create a new window where the same presentation will be displayed. This window is linked to the main window. Changing slides on one will cause the slide to change on the other. Useful when presenting. --- ## Requirements Before diving into this slide deck, we recommend you to have a look at: - [Introduction to Galaxy Analyses](/training-material/topics/introduction) - [Sequence analysis](/training-material/topics/sequence-analysis) - Quality Control: [<i class="fab fa-slideshare" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="visually-hidden">slides</span> slides](/training-material/topics/sequence-analysis/tutorials/quality-control/slides.html) - [<i class="fas fa-laptop" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="visually-hidden">tutorial</span> hands-on](/training-material/topics/sequence-analysis/tutorials/quality-control/tutorial.html) - Mapping: [<i class="fab fa-slideshare" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="visually-hidden">slides</span> slides](/training-material/topics/sequence-analysis/tutorials/mapping/slides.html) - [<i class="fas fa-laptop" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="visually-hidden">tutorial</span> hands-on](/training-material/topics/sequence-analysis/tutorials/mapping/tutorial.html) --- ### <i class="far fa-question-circle" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="visually-hidden">question</span> Questions - What is ChIP-seq? --- ### <i class="fas fa-bullseye" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="visually-hidden">objectives</span> Objectives - Identify ChIP-seq data --- ## ChIP-seq - **Ch**romatin **I**mmuno**P**recipitation combined with **seq**uencing - Identifying the location of proteins binding sites - Transcription Factors - Histone modifications - 2 Types of sequenced data - ChIP data - Input data .image-75[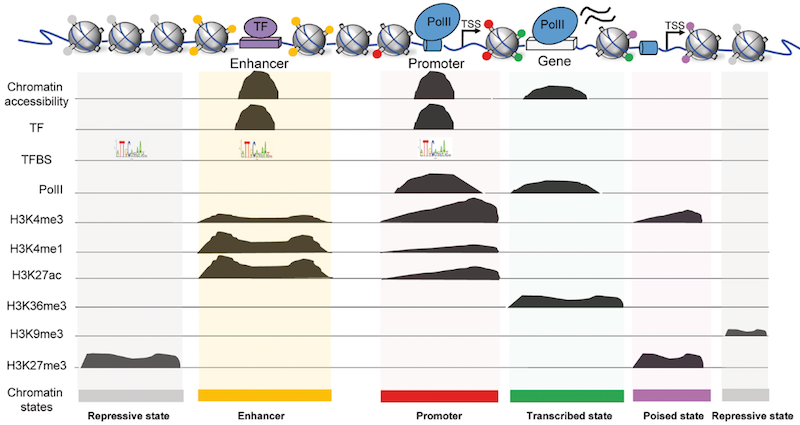] --- ## Generating ChIP-seq data 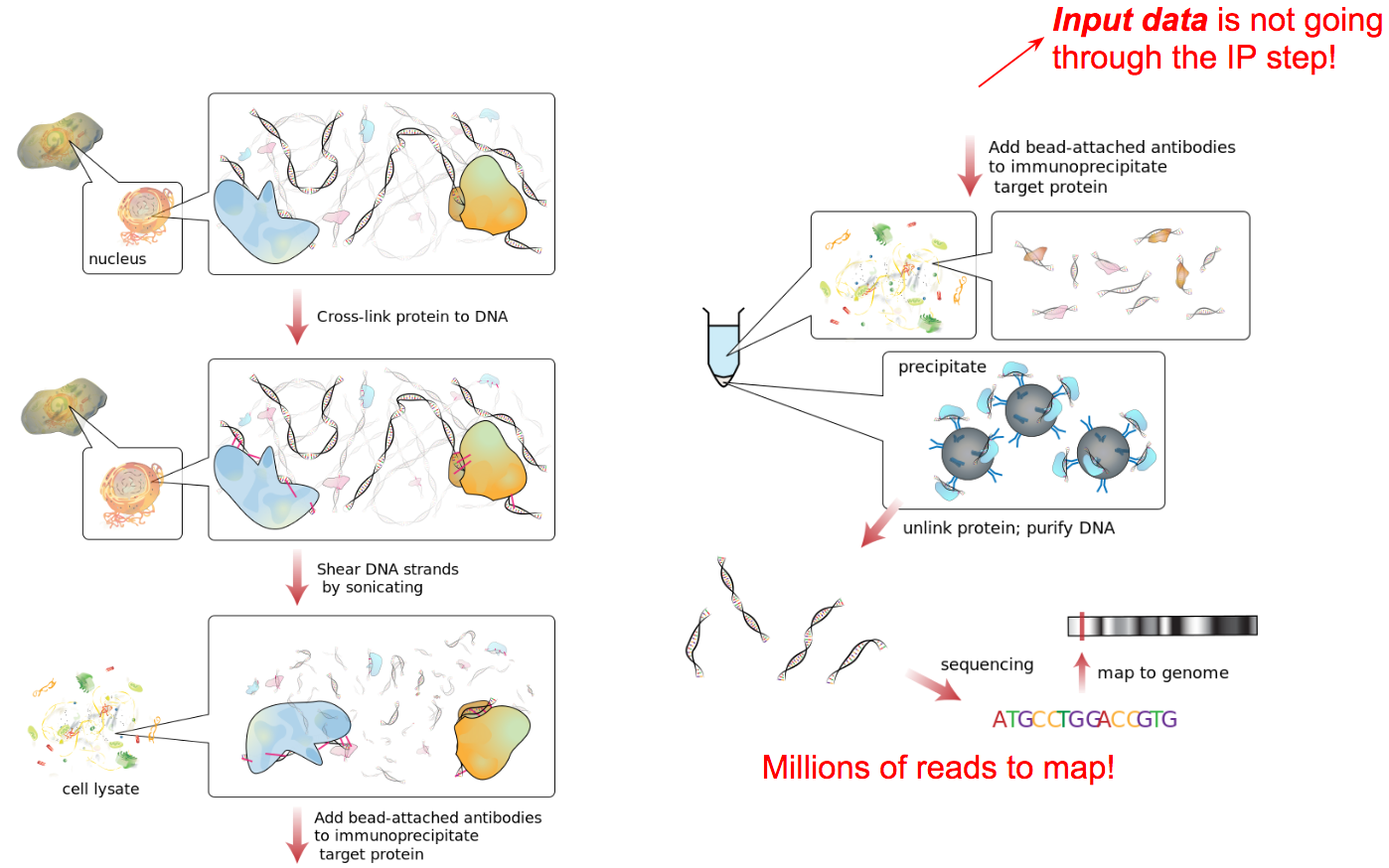 <small> Source: [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ChIP-sequencing ) </small> --- ## ChIP vs Input 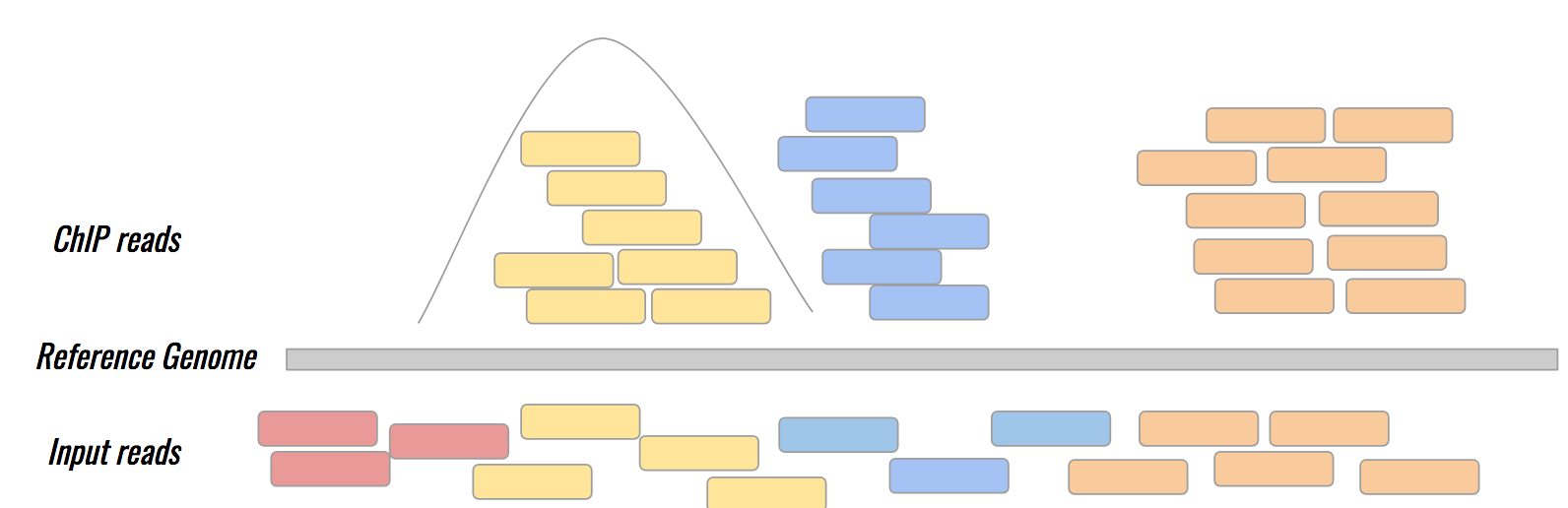 --- 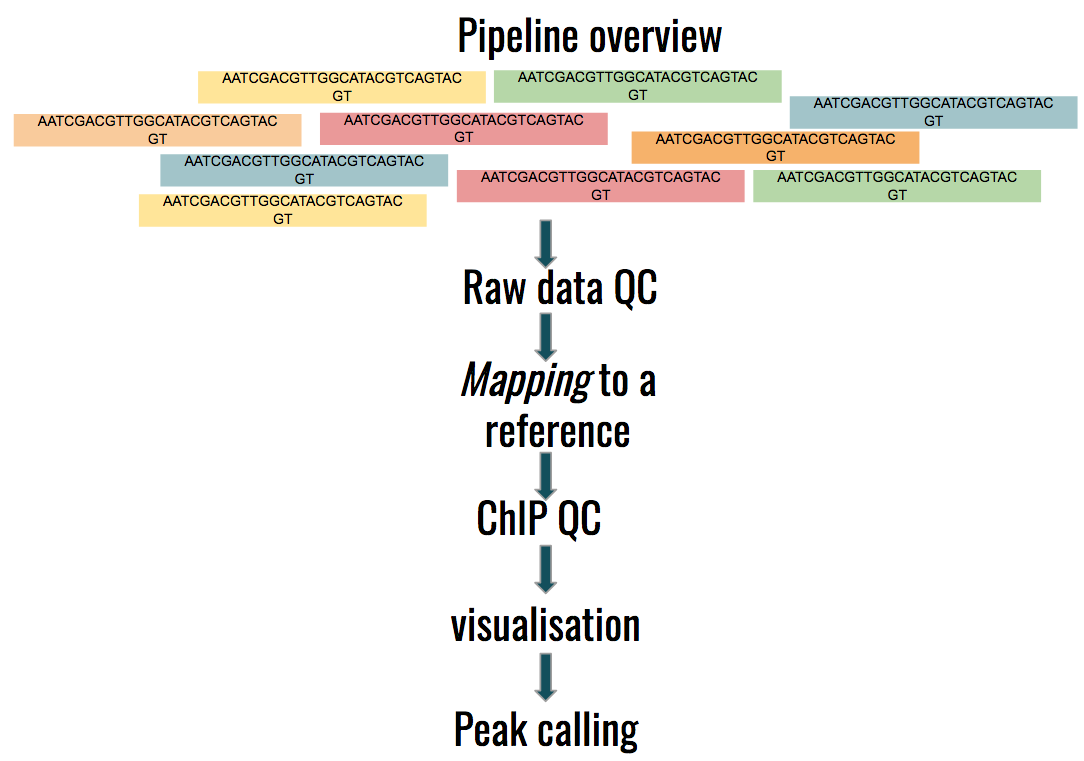 --- ## Studying the effect of SCHMD1 protein in chromosome X SCHMD1 in known to have an effect on gene expression in X chromosome  Chen-Yu Wang et al. 2018; Vivek Bhardwaj, Steffen Heyne et al. 2018 ??? We probe a potential architectural role for SMCHD1 and investigate the mechanism by which it shapes the Xi and represses gene expression --- ### <i class="fas fa-key" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="visually-hidden">keypoints</span> Key points - --- ## Thank You! This material is the result of a collaborative work. Thanks to the [Galaxy Training Network](https://training.galaxyproject.org) and all the contributors! <div markdown="0"> <div class="contributors-line"> Authors: <a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/LeilyR/" class="contributor-badge contributor-LeilyR"><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/LeilyR?s=27" alt="Avatar">Leily Rabbani</a> <a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/bebatut/" class="contributor-badge contributor-bebatut"><img src="/training-material/assets/images/orcid.png" alt="orcid logo"/><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/bebatut?s=27" alt="Avatar">Bérénice Batut</a> </div> </div> <div style="display: flex;flex-direction: row;align-items: center;justify-content: center;"> <img src="/training-material/assets/images/GTN.png" alt="Galaxy Training Network" style="height: 100px;"/> </div> <a rel="license" href="https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/"> This material is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License</a>.