Training Infrastructure as a Service (TIaaS)


OverviewQuestions:Objectives:
How to deploy EU’s TIaaS
Requirements:
Setup TIaaS
Request and manage trainings
Join a training
- Galaxy Server administration
- Ansible: slides slides - tutorial hands-on
- Galaxy Installation with Ansible: slides slides - tutorial hands-on
- Connecting Galaxy to a compute cluster: slides slides - tutorial hands-on
- Mapping Jobs to Destinations: tutorial hands-on
- Running Jobs on Remote Resources with Pulsar: slides slides - tutorial hands-on
Time estimation: 30 minutesSupporting Materials:Last modification: Oct 18, 2022
Galaxy is widely used for teaching. In order to facilitate instructors, Galaxy Europe has developed Training Infrastructure as a Service (TIaaS). Workshop instructors can apply for TIaaS, and on the day of their workshop, their participants will be placed in a special group and use dedicated resources, thus reducing queue times on the day of the training.
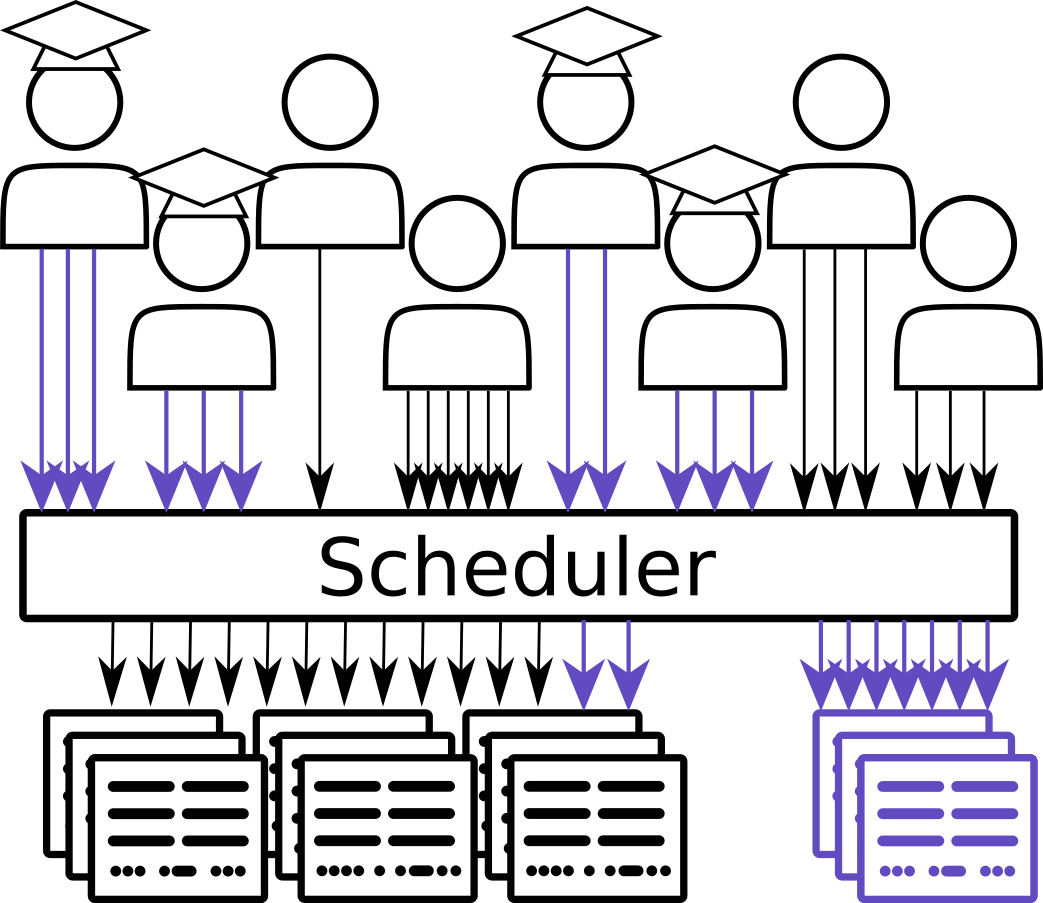
This tutorial will go cover how to set up such a service on your own Galaxy server.
Agenda
Comment: Galaxy Admin Training PathThe yearly Galaxy Admin Training follows a specific ordering of tutorials. Use this timeline to help keep track of where you are in Galaxy Admin Training.
Setting up TIaaS
Hands-on: Setup TIaaS
In your
requirements.ymladd the TIaaS ansible role:--- a/requirements.yml +++ b/requirements.yml @@ -36,3 +36,5 @@ version: 0.14.2 - src: dj-wasabi.telegraf version: 0.12.0 +- src: usegalaxy_eu.tiaas2 + version: 0.0.8And run the install step:
Input: Bashansible-galaxy install -p roles -r requirements.ymlIf you haven’t worked with diffs before, this can be something quite new or different.
If we have two files, let’s say a grocery list, in two files. We’ll call them ‘a’ and ‘b’.
Old $ cat old
🍎
🍐
🍊
🍋
🍒
🥑New $ cat new
🍎
🍐
🍊
🍋
🍍
🥑We can see that they have some different entries. We’ve removed 🍒 because they’re awful, and replaced them with an 🍍
Diff lets us compare these files
$ diff old new
5c5
< 🍒
---
> 🍍Here we see that 🍒 is only in a, and 🍍 is only in b. But otherwise the files are identical.
There are a couple different formats to diffs, one is the ‘unified diff’
$ diff -U2 old new
--- old 2022-02-16 14:06:19.697132568 +0100
+++ new 2022-02-16 14:06:36.340962616 +0100
@@ -3,4 +3,4 @@
🍊
🍋
-🍒
+🍍
🥑This is basically what you see in the training materials which gives you a lot of context about the changes:
--- oldis the ‘old’ file in our view+++ newis the ‘new’ file- @@ these lines tell us where the change occurs and how many lines are added or removed.
- Lines starting with a - are removed from our ‘new’ file
- Lines with a + have been added.
So when you go to apply these diffs to your files in the training:
- Ignore the header
- Remove lines starting with - from your file
- Add lines starting with + to your file
The other lines (🍊/🍋 and 🥑) above just provide “context”, they help you know where a change belongs in a file, but should not be edited when you’re making the above change. Given the above diff, you would find a line with a 🍒, and replace it with a 🍍
Added & Removed Lines
Removals are very easy to spot, we just have removed lines
--- old 2022-02-16 14:06:19.697132568 +0100
+++ new 2022-02-16 14:10:14.370722802 +0100
@@ -4,3 +4,2 @@
🍋
🍒
-🥑And additions likewise are very easy, just add a new line, between the other lines in your file.
--- old 2022-02-16 14:06:19.697132568 +0100
+++ new 2022-02-16 14:11:11.422135393 +0100
@@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
🍎
+🍍
🍐
🍊Completely new files
Completely new files look a bit different, there the “old” file is
/dev/null, the empty file in a Linux machine.$ diff -U2 /dev/null old
--- /dev/null 2022-02-15 11:47:16.100000270 +0100
+++ old 2022-02-16 14:06:19.697132568 +0100
@@ -0,0 +1,6 @@
+🍎
+🍐
+🍊
+🍋
+🍒
+🥑And removed files are similar, except with the new file being /dev/null
--- old 2022-02-16 14:06:19.697132568 +0100
+++ /dev/null 2022-02-15 11:47:16.100000270 +0100
@@ -1,6 +0,0 @@
-🍎
-🍐
-🍊
-🍋
-🍒
-🥑In your
galaxyserversgroup variables file, add the following:--- a/group_vars/galaxyservers.yml +++ b/group_vars/galaxyservers.yml @@ -234,6 +234,15 @@ telegraf_plugins_extra: - data_format = "influx" - interval = "15s" +# TIaaS setup +tiaas_dir: /opt/tiaas +tiaas_user: tiaas +tiaas_group: tiaas +tiaas_version: master +tiaas_admin_user: admin +tiaas_admin_pass: changeme +tiaas_listen_url: "127.0.0.1:6000" + # TUS galaxy_tusd_port: 1080 tusd_instances:In the
galaxyserversgroup variables file, we also need to set the database permissions correctly for TIaaS. It needs to be able to access some Galaxy tables, and we will carefully define only the ones we really need:--- a/group_vars/galaxyservers.yml +++ b/group_vars/galaxyservers.yml @@ -8,6 +8,7 @@ pip_package: python3-pip # geerlingguy.pip postgresql_objects_users: - name: galaxy - name: telegraf + - name: tiaas postgresql_objects_databases: - name: galaxy owner: galaxy @@ -16,6 +17,27 @@ postgresql_objects_privileges: roles: telegraf privs: SELECT objs: ALL_IN_SCHEMA + - database: galaxy + roles: tiaas + objs: galaxy_user,galaxy_session,job,history,workflow,workflow_invocation + type: table + privs: SELECT + - database: galaxy + roles: tiaas + objs: user_group_association,galaxy_group,role,group_role_association + type: table + privs: SELECT,INSERT + - database: galaxy + roles: tiaas + objs: group_role_association + type: table + privs: DELETE + - database: galaxy + roles: tiaas + objs: role_id_seq,galaxy_group_id_seq,group_role_association_id_seq,user_group_association_id_seq + type: sequence + privs: USAGE,SELECT + # PostgreSQL Backups postgresql_backup_dir: /data/backups postgresql_backup_local_dir: "{{ '~postgres' | expanduser }}/backups"The
DELETEprivilege is limited in scope to one table:group_role_association. This allows TIaaS to disassociate training groups from roles in the Galaxy database after the training event date has passed, so that users who participated in a training return to using normal (non-training) resources after the training ends.The
usegalaxy_eu.tiaas2role will create a cron job to perform this process every night at midnight. You can control when this runs (or disable it) using the tiaas_disassociate_training_roles variable.We need to add the
usegalaxy_eu.tiaas2role to the end of the playbook (galaxy.yml)--- a/galaxy.yml +++ b/galaxy.yml @@ -35,3 +35,4 @@ - galaxyproject.cvmfs - galaxyproject.gxadmin - dj-wasabi.telegraf + - usegalaxy_eu.tiaas2Lastly we should add the routes for TIaaS to the NGINX template for Galaxy:
--- a/templates/nginx/galaxy.j2 +++ b/templates/nginx/galaxy.j2 @@ -90,4 +90,19 @@ server { proxy_set_header Host $http_host; } + location /tiaas { + uwsgi_pass {{ tiaas_listen_url }}; + uwsgi_param UWSGI_SCHEME $scheme; + include uwsgi_params; + } + + location /tiaas/static { + alias /opt/tiaas/static; + } + + location /join-training { + uwsgi_pass {{ tiaas_listen_url }}; + uwsgi_param UWSGI_SCHEME $scheme; + include uwsgi_params; + } }Run the playbook
Input: Bashansible-playbook galaxy.yml
1.sh
TIaaS should be available now! The following routes on your server are now configured (we will run through these in the next section)
| URL | Use | Who |
|---|---|---|
| https://<server>/tiaas/new/ | Request a new TIaaS training | Instructors |
| https://<server>/tiaas/admin/ | Approve and Manage requests | Admin |
| https://<server>/tiaas/stats/ | Overall TIaaS statistics (EU Stats) | Admins, Funding Agencies |
| https://<server>/tiaas/calendar/ | Calendar of trainings (EU Calendar) | Admins, Funding Agencies |
| https://<server>/join-training/<training-id> | Join an TIaaS training | Participants |
| https://<server>/join-training/<training-id>/status | Dashboard with job states of trainees. | Instructors |
Let’s see it in action!
Hands-on: Using TIaaS
- Create a new TIaaS request
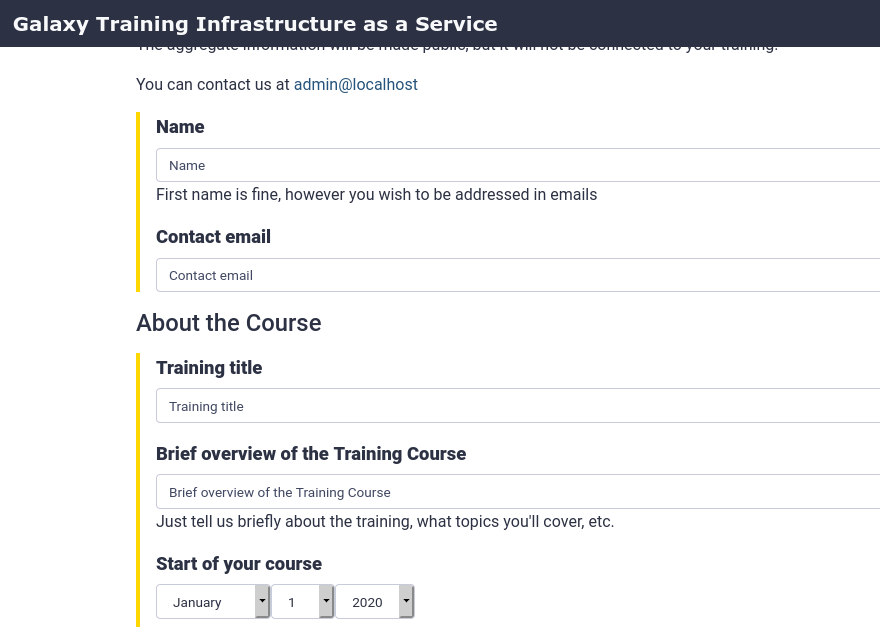
- Go to https://<server>/tiaas/new/
- Here you will find the request form users will fill in to request TIaaS:
- For “Training Identifier”, fill in
gryffindor(or remember this value if you enter something different)
- This is the
<training-id>used in the URLs listed above used for:
- Workshop participants to join the tiaas group
- Workshop instructors to monitor the progress of their participants.
- Fill in the rest of the form as you like
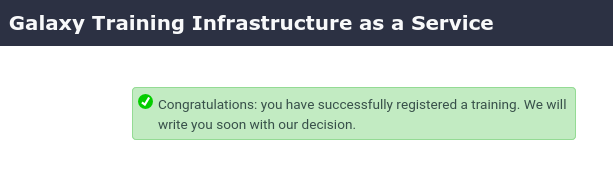
- Submit the form and you should see a confirmation dialog:
- Approve TIaaS request
- Next, the request will have to be approved by an admin
- Go to https://<server>/tiaas/admin
- Log in using the values you configured
tiaas_admin_userandtiaas_admin_passin your group variables file
- Default values were
admin:changeme- You should now see the admin panel:
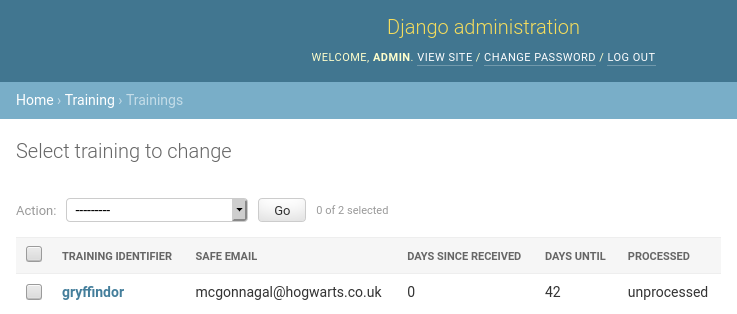
- Click on Trainings, you should see the TIaaS request listed here:
- Approve the request
- Click on the training
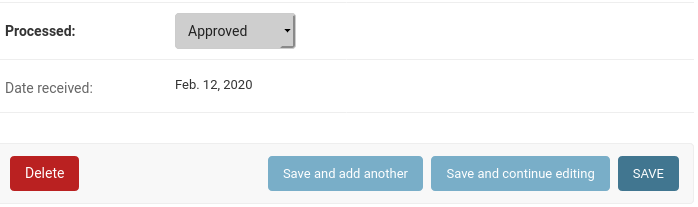
- Scroll down to the bottom
- Change “Processed” to
Approvedand Save- At this point, you would likely email the person who made the request to inform them of approval
- Join TIaaS Training
- Make sure you are logged in to Galaxy
- On the day of the workshop, participants will visit a following URL to join the TIaaS group
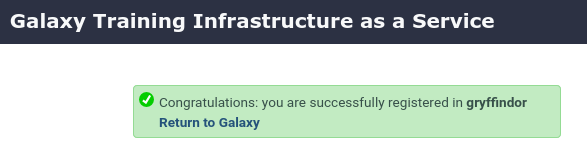
- https://<server>/join-training/gryffindor
- A confirmation dialog should appear if all went well:
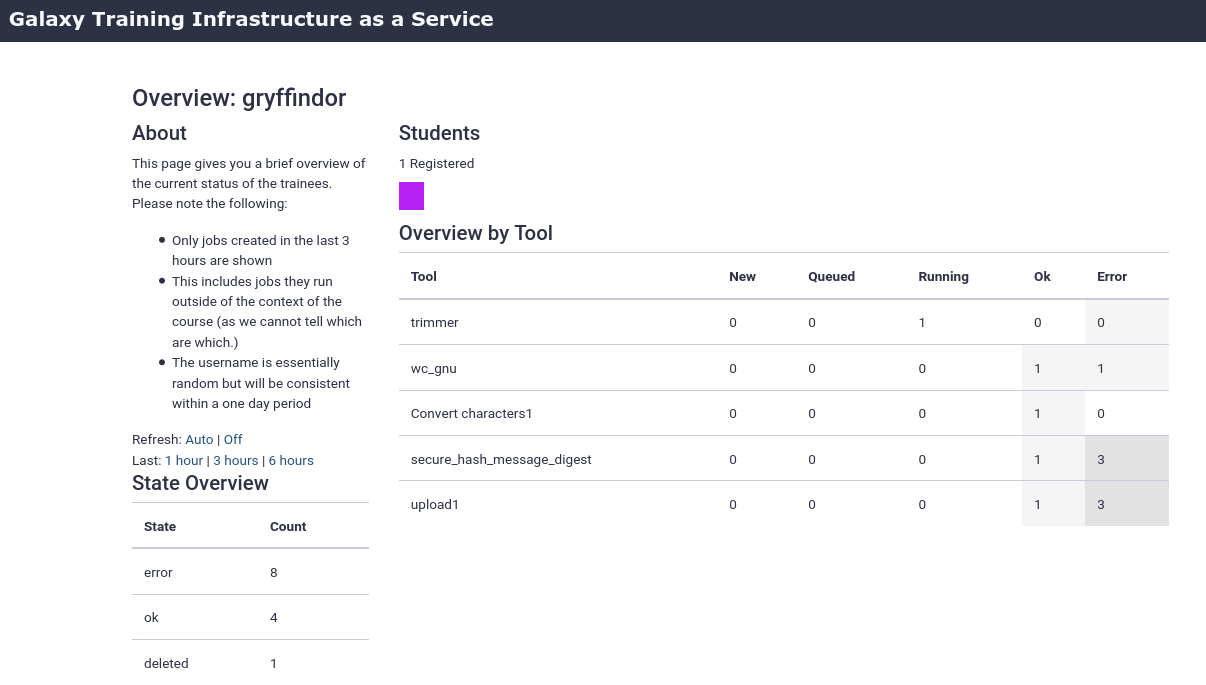
- Monitor TIaaS status
- This is very useful for instructors to monitor the job state of their participants
- Go to https://<server>/join-training/gryffindor/status
- In the Dasboard you should see that one user (you) has joined the training \
- Run some jobs to see the dashboard in action
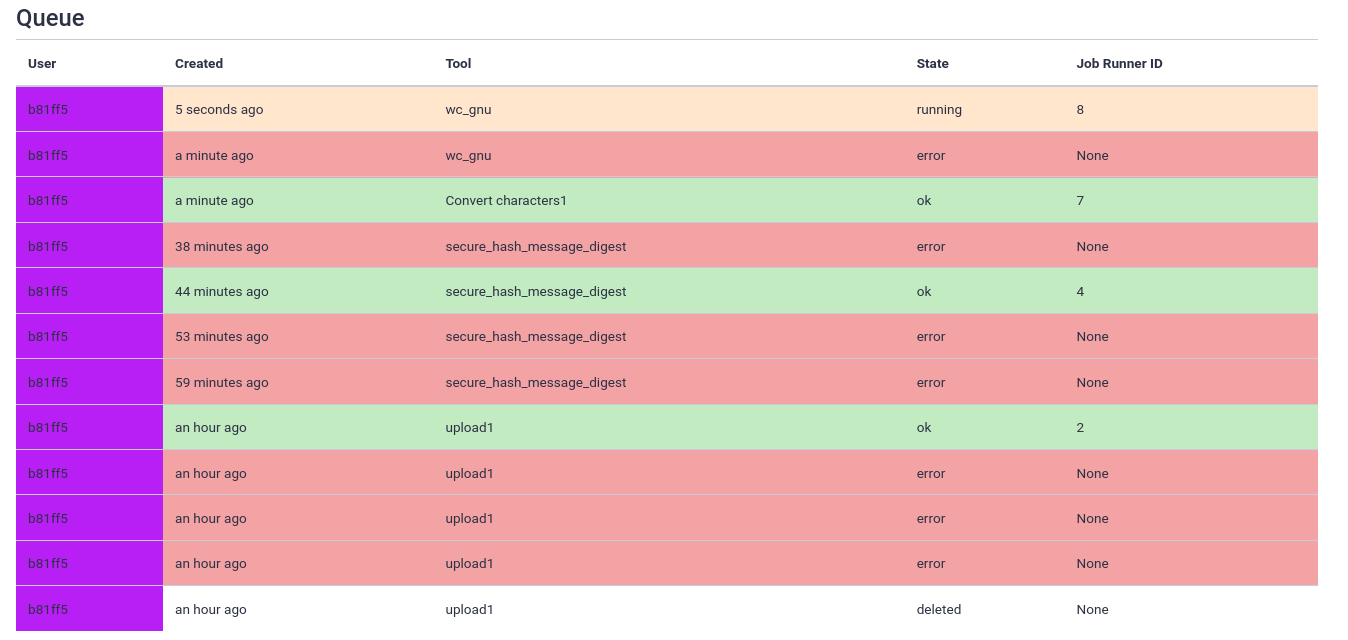
- Scroll down to get some more information on a per-user level (anonymized)
- Every user designated by their own identifier and colour, but no personal information
Comment: Note: GDPR assistanceSince this setup tracks additional personal information (submitter name & email, users in the queue view), TIaaS includes some always-on features to assist with your GDPR compliance.
- Users in public status dashboard are only visible by an anonymized identifier and colour
- Email addressses in the TIaaS admin panel will be automatically expunged 60 days after a training event
Of course you need to review any GDPR compliance concerns with your group’s legal representative(s), this only attempts to ensure some protections exist for the users of the system.
Job Configuration
While observability for teachers or trainers is already a huge benefit, one of the primary benefits of TIaaS from UseGalaxy.eu is that your jobs get sent to dedicated compute resources, which won’t be used by anyone else, during the period of the training. We will send all of the training jobs to pulsar if you have completed that tutorial, or one of the slurm destinations from the job configuration training.
In order to achieve this, we first need some way to sort the jobs of the training users into these private queues, while letting the other jobs continue on. So let’s create a sorting hat to figure out where jobs belong.
Hands-on: Writing a dynamic job destination
Create and open
templates/galaxy/dynamic_job_rules/hogwarts.py--- /dev/null +++ b/templates/galaxy/dynamic_job_rules/hogwarts.py @@ -0,0 +1,19 @@ +from galaxy.jobs import JobDestination +from galaxy.jobs.mapper import JobMappingException +import os + +def sorting_hat(app, user): + # Check that the user is not anonymous + if not user: + return app.job_config.get_destination('slurm') + + # Collect the user's roles + user_roles = [role.name for role in user.all_roles() if not role.deleted] + + # If any of these are prefixed with 'training-' + if any([role.startswith('training-') for role in user_roles]): + # Then they are a training user, we will send their jobs to pulsar, + # Or give them extra resources + return app.job_config.get_destination('slurm-2c') # or pulsar, if available + + return app.job_config.get_destination('slurm')This destination will check that the
user_emailis in a training group (role starting withtraining-).As usual, we need to instruct Galaxy of where to find this file. Edit your group variables file and add the following:
--- a/group_vars/galaxyservers.yml +++ b/group_vars/galaxyservers.yml @@ -137,6 +137,7 @@ galaxy_local_tools: galaxy_dynamic_job_rules: - my_rules.py - map_resources.py +- hogwarts.py # systemd galaxy_manage_systemd: trueWe next need to configure this plugin in our job configuration (
templates/galaxy/config/job_conf.yml.j2):--- a/templates/galaxy/config/job_conf.yml.j2 +++ b/templates/galaxy/config/job_conf.yml.j2 @@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ runners: manager: _default_ execution: - default: slurm + default: sorting_hat environments: local_dest: runner: local_runner @@ -73,6 +73,10 @@ execution: dynamic_cores_time: runner: dynamic function: dynamic_cores_time + # Next year this will be replaced with the TPV. + sorting_hat: + runner: dynamic + function: sorting_hat resources: default: defaultThis is a Python function dynamic destination. Galaxy will load all python files in the
{{ galaxy_dynamic_rule_dir }}, and all functions defined in those will be available to be used in thejob_conf.yml.j2. Additionally it will send all jobs through the sorting hat, but we want upload jobs to stay local. They should always run locally.Run the playbook
Input: Bashansible-playbook galaxy.ymlEnsure your user is joined to a training
Run a job and observe the logs to see where it goes (
journalctl -u galaxy -f)
Congratulations! you have now set up TIaaS on your Galaxy server.
2.sh
Comment: Got lost along the way?If you missed any steps, you can compare against the reference files, or see what changed since the previous tutorial.
If you’re using
gitto track your progress, remember to add your changes and commit with a good commit message!
Key points
TIaaS is an additional service you can deploy which can help you provide a better service to your users
Frequently Asked Questions
Have questions about this tutorial? Check out the tutorial FAQ page or the FAQ page for the Galaxy Server administration topic to see if your question is listed there. If not, please ask your question on the GTN Gitter Channel or the Galaxy Help ForumFeedback
Did you use this material as an instructor? Feel free to give us feedback on how it went.
Did you use this material as a learner or student? Click the form below to leave feedback.
Citing this Tutorial
- Helena Rasche, Saskia Hiltemann, 2022 Training Infrastructure as a Service (TIaaS) (Galaxy Training Materials). https://training.galaxyproject.org/training-material/topics/admin/tutorials/tiaas/tutorial.html Online; accessed TODAY
- Batut et al., 2018 Community-Driven Data Analysis Training for Biology Cell Systems 10.1016/j.cels.2018.05.012
Congratulations on successfully completing this tutorial!@misc{admin-tiaas, author = "Helena Rasche and Saskia Hiltemann", title = "Training Infrastructure as a Service (TIaaS) (Galaxy Training Materials)", year = "2022", month = "10", day = "18" url = "\url{https://training.galaxyproject.org/training-material/topics/admin/tutorials/tiaas/tutorial.html}", note = "[Online; accessed TODAY]" } @article{Batut_2018, doi = {10.1016/j.cels.2018.05.012}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.cels.2018.05.012}, year = 2018, month = {jun}, publisher = {Elsevier {BV}}, volume = {6}, number = {6}, pages = {752--758.e1}, author = {B{\'{e}}r{\'{e}}nice Batut and Saskia Hiltemann and Andrea Bagnacani and Dannon Baker and Vivek Bhardwaj and Clemens Blank and Anthony Bretaudeau and Loraine Brillet-Gu{\'{e}}guen and Martin {\v{C}}ech and John Chilton and Dave Clements and Olivia Doppelt-Azeroual and Anika Erxleben and Mallory Ann Freeberg and Simon Gladman and Youri Hoogstrate and Hans-Rudolf Hotz and Torsten Houwaart and Pratik Jagtap and Delphine Larivi{\`{e}}re and Gildas Le Corguill{\'{e}} and Thomas Manke and Fabien Mareuil and Fidel Ram{\'{\i}}rez and Devon Ryan and Florian Christoph Sigloch and Nicola Soranzo and Joachim Wolff and Pavankumar Videm and Markus Wolfien and Aisanjiang Wubuli and Dilmurat Yusuf and James Taylor and Rolf Backofen and Anton Nekrutenko and Björn Grüning}, title = {Community-Driven Data Analysis Training for Biology}, journal = {Cell Systems} }
 Questions:
Questions: