What is Taxonomy?
Taxonomy is the method used to naming, defining (circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics such as morphological characteristics, phylogenetic characteristics, DNA data, etc. It is founded on the concept that the similarities descend from a common evolutionary ancestor.
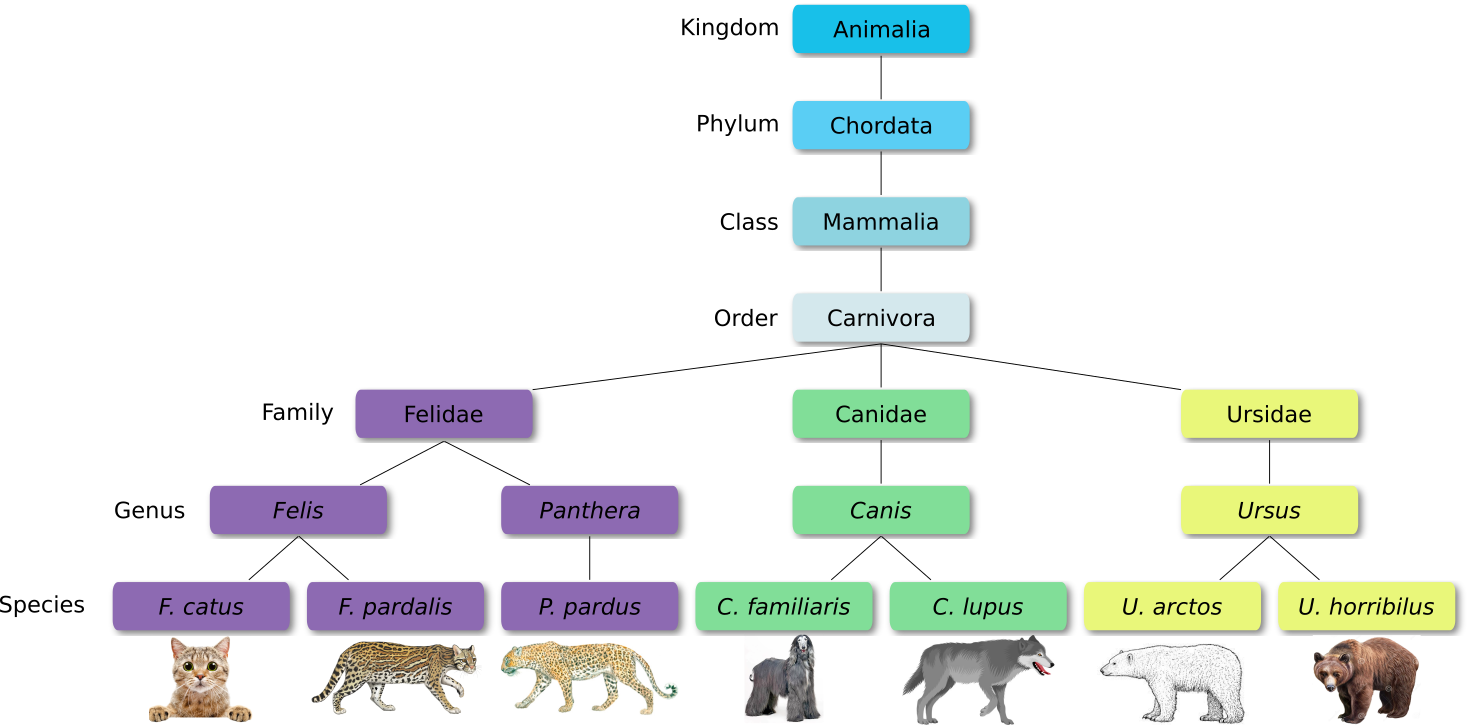
Defined groups of organisms are known as taxa. Taxa are given a taxonomic rank and are aggregated into super groups of higher rank to create a taxonomic hierarchy. The taxonomic hierarchy includes eight levels: Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus and Species.
The classification system begins with 3 domains that encompass all living and extinct forms of life
- The Bacteria and Archae are mostly microscopic, but quite widespread.
- Domain Eukarya contains more complex organisms
When new species are found, they are assigned into taxa in the taxonomic hierarchy. For example for the cat:
| Level | Classification |
|---|---|
| Domain | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Mammalia |
| Order | Carnivora |
| Family | Felidae |
| Genus | Felis |
| Species | F. catus |
Let’s explore taxonomy in the Tree of Life, using Lifemap
Still have questions?
Want to embed this snippet (FAQ) in your GTN Tutorial?
{% snippet topics/metagenomics/faqs/taxon.md %}
