Nucleoli Segmentation
&
Feature Extraction
using CellProfiler
Contributors

Questions
How do I run an image analysis pipeline on public data using CellProfiler?
How do I analyse the DNA channel of fluorescence siRNA screens?
How do I download public image data into my history?
How do I segment and label cell nuclei?
How do I segment nucleoli (as the absence of DNA)?
How do I combine nuclei and nucleoli into one segmentation mask?
How do I extract the background of an image?
How do I relate the nucleoli to their parent nucleus?
How do I measure the image and object features?
How do I measure the image quality?
Objectives
How to download images from a public image repository.
How to segment cell nuclei using CellProfiler in Galaxy.
How to segment cell nucleoli using CellProfiler in Galaxy.
How to extract features for images, nuclei and nucleoli.
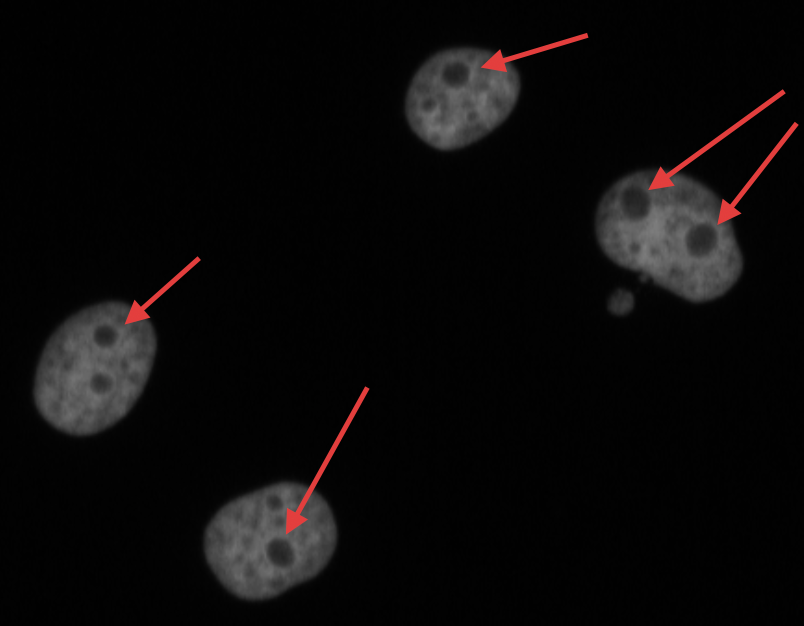
What is the nucleoli?
- Membrane-less organelle in the nucleus of the cell
- Functions: ribosome biogenesis and cell cycle regulation
.image-55[
 ]
]
Speaker Notes In the DNA channel, the nucleoli is shown as the absence of DNA (red arrows). —
Data
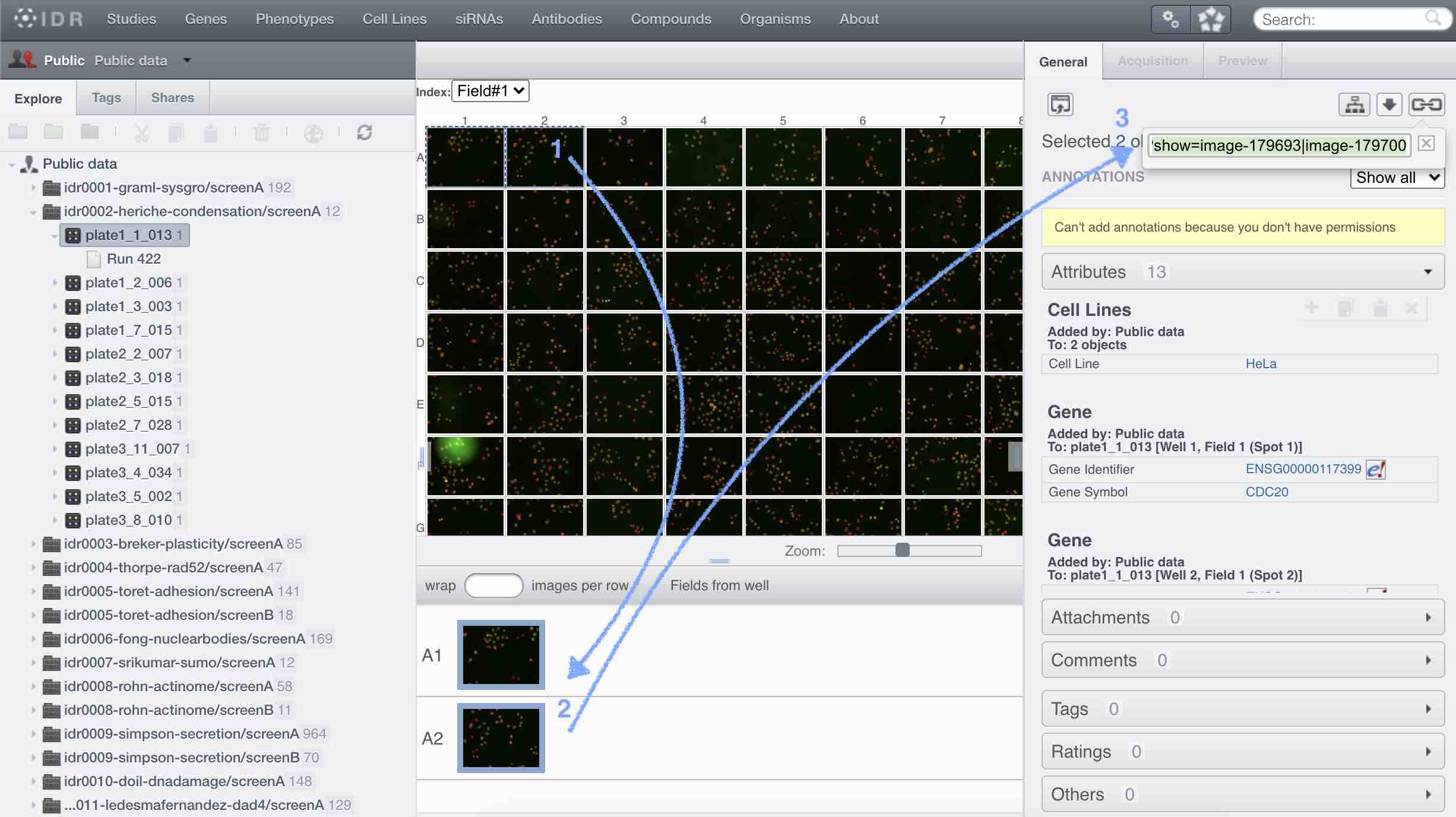
- The data can be downloaded from the Image Data Resource (IDR)
.image-65[
 ]
]
Speaker Notes In the IDR the images can be selected in the user interface (1). The images will then show up at the bottom (2) where they need to be selected once again and then copy the URL from the link icon on the top left (3). That URL contains the image ids that will be downloaded. You can also bring your images by uploading the DNA channel of your images to your Galaxy history. —
General Workflow
- The workflow contains 4 basic parts:
- Segmentation of the nuclei
- Segmentation of the nucleoli that fall inside the nuclei
- Background detection
- Feature extraction of the images and objects
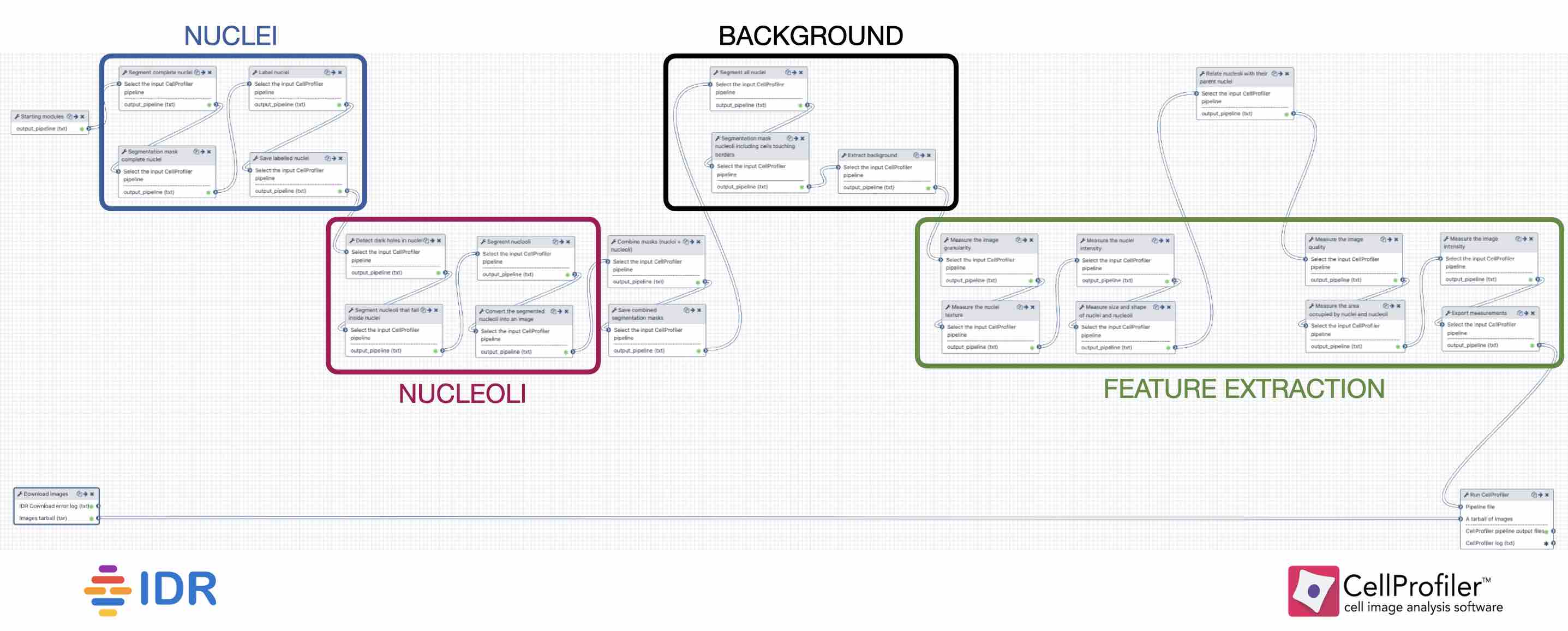
Speaker Notes
- Segmentation of the nucleoli: since there is no staining for the nucleoli, the holes need to be detected and segmented.
- Feature extraction: the order of the tools does not affect the outcome.
-
Background detection: Detection of the foreground and subtraction from the image.
1) Segment nuclei
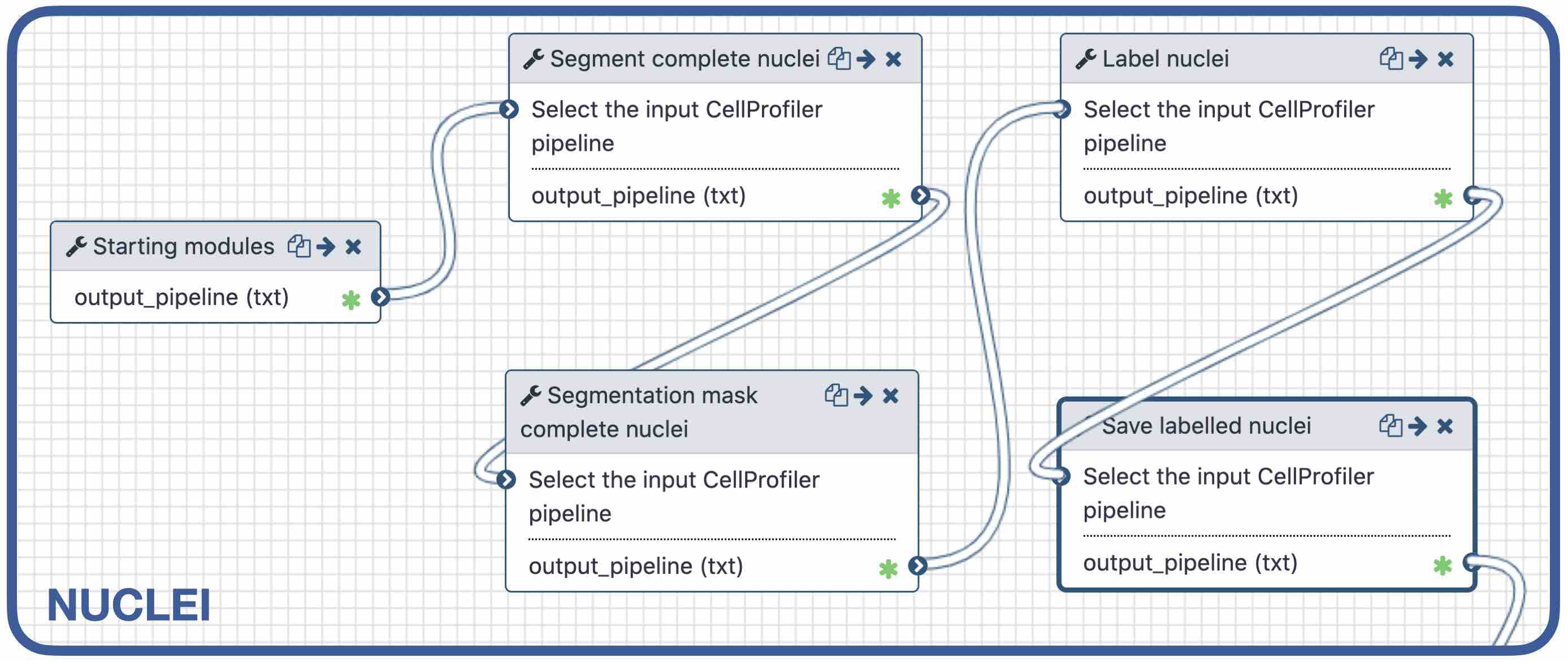
Speaker Notes Every CellProfiler pipeline needs to start by processing the metadata with the tool “Starting modules”.
- Segment complete nuclei: this tool identifies the nuclei within a certain size and excludes those cells that are touching the borders of the image.
- Segmentation mask complete nuclei: gathers all the nuclei identified in the previous step in one mask.
- Label and save labelled nuclei: adds the id of each nucleus on top of it. This can be useful later for a proper interpretation of the data analysis.—
Segmentation and labelling of the nuclei
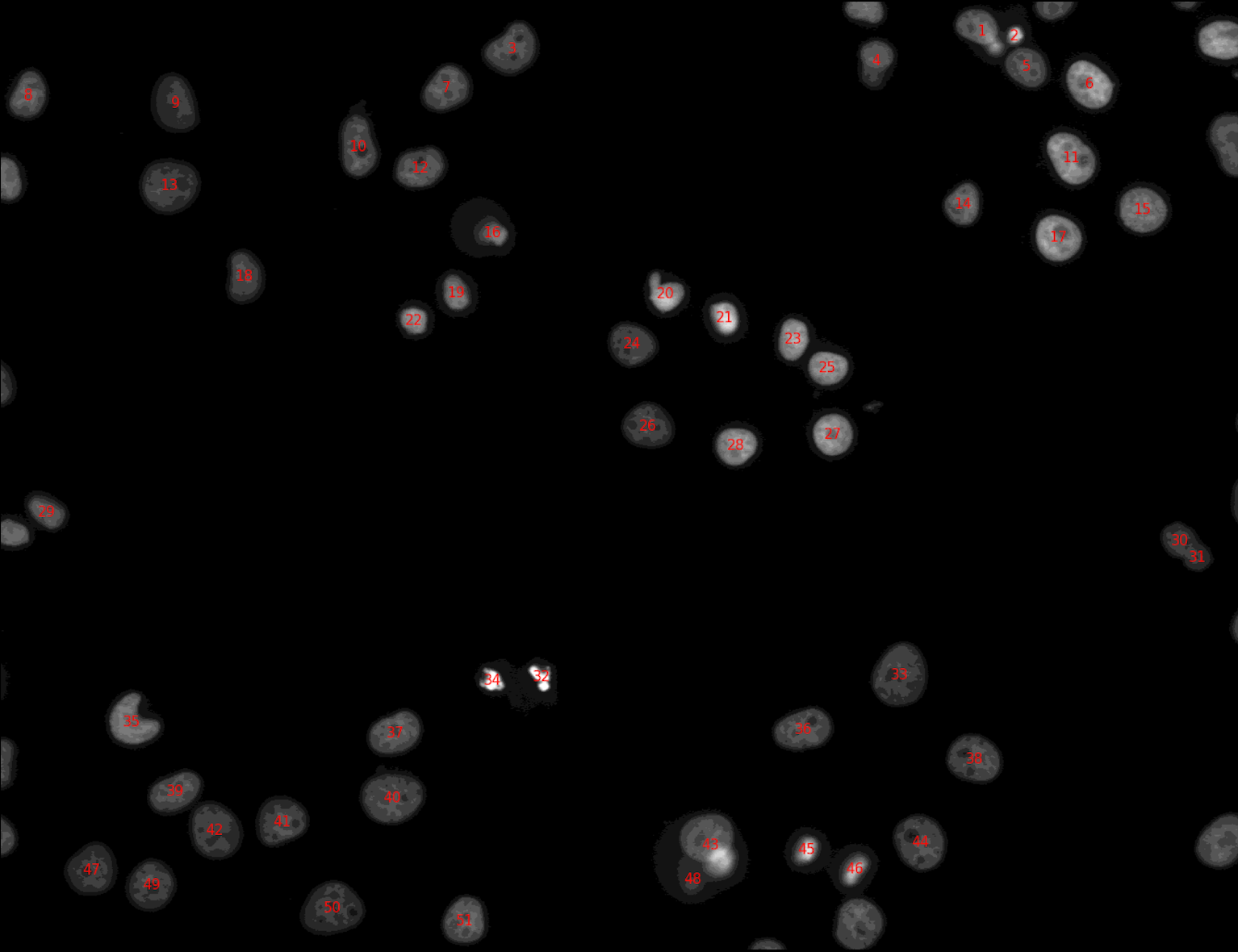
Speaker Notes Resulting image after the first logical step of the workflow in which the nuclei were segmented and labelled. —
2) Segment nucleoli
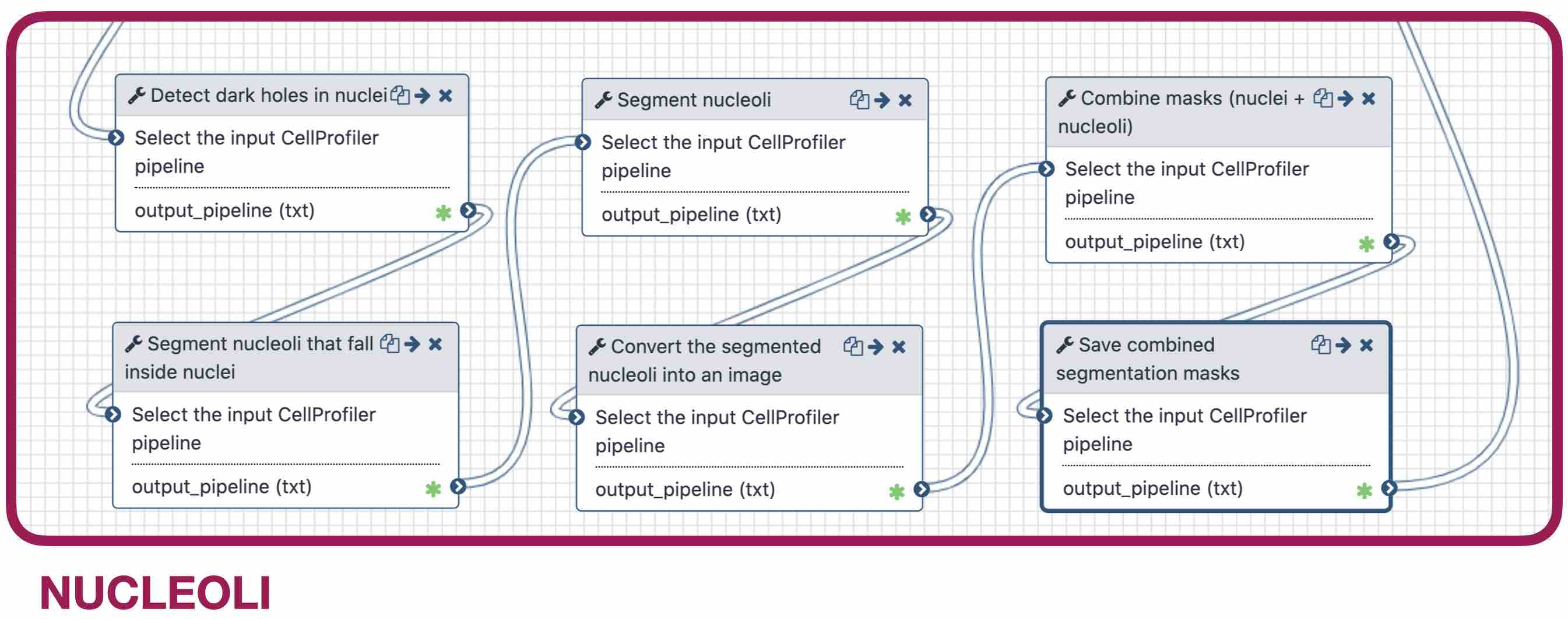
Speaker Notes To identify the nucleoli the first step is to enhance the dark holes so that they can be segmented. The segmentation of the dark holes will take place only when the dark holes fall inside a nucleus. This is to avoid the detection of wrong objects outside the cell. At this step, the segmentation of the nucleoli can be performed. It will be useful for visual exploration that the masks of the nuclei and nucleoli are saved together into one segmentation mask. —
Combined mask: nuclei + nucleoli
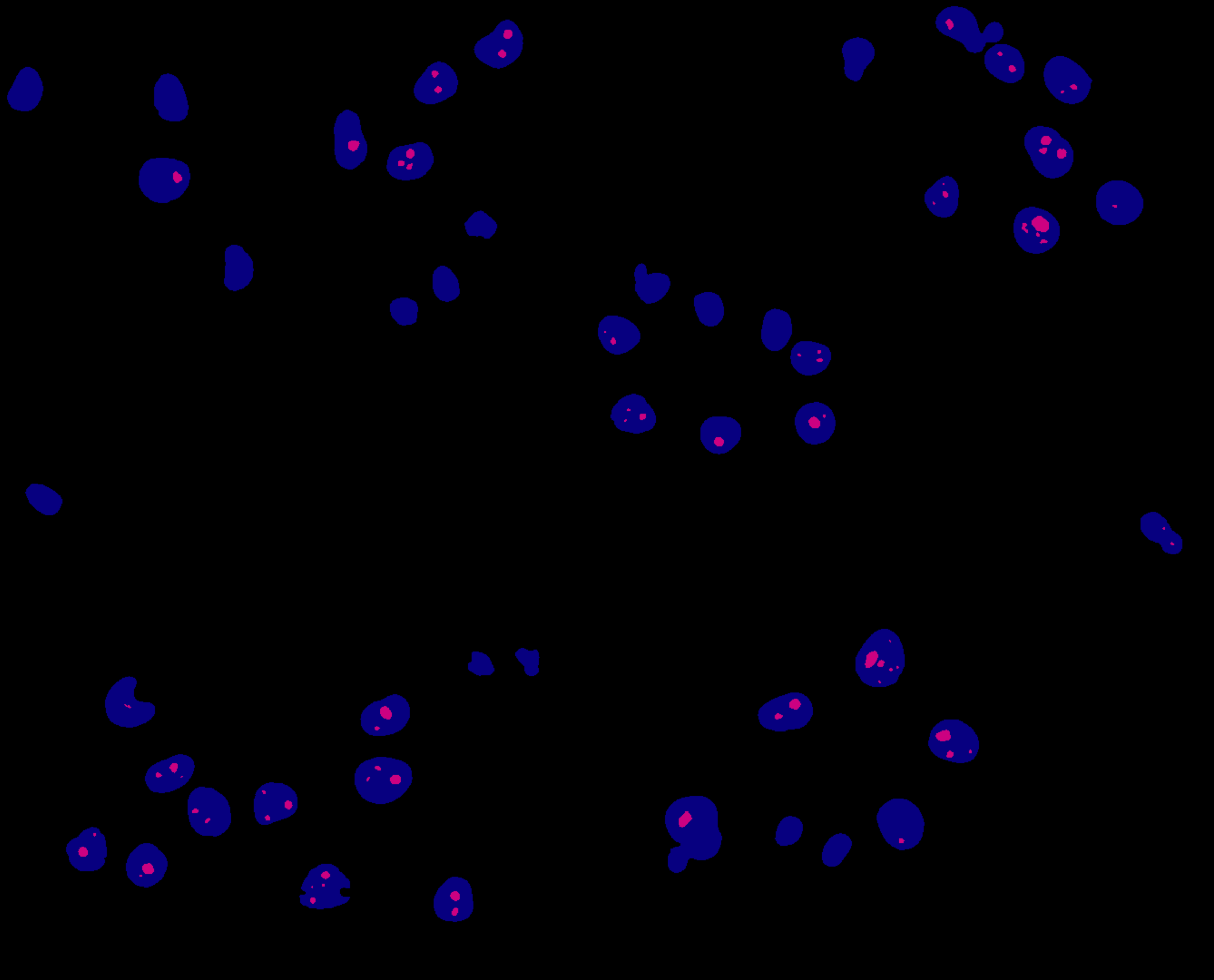
Speaker Notes The combination of both masks gives an image with the nuclei in blue and the nucleoli in magenta. —
Background extraction
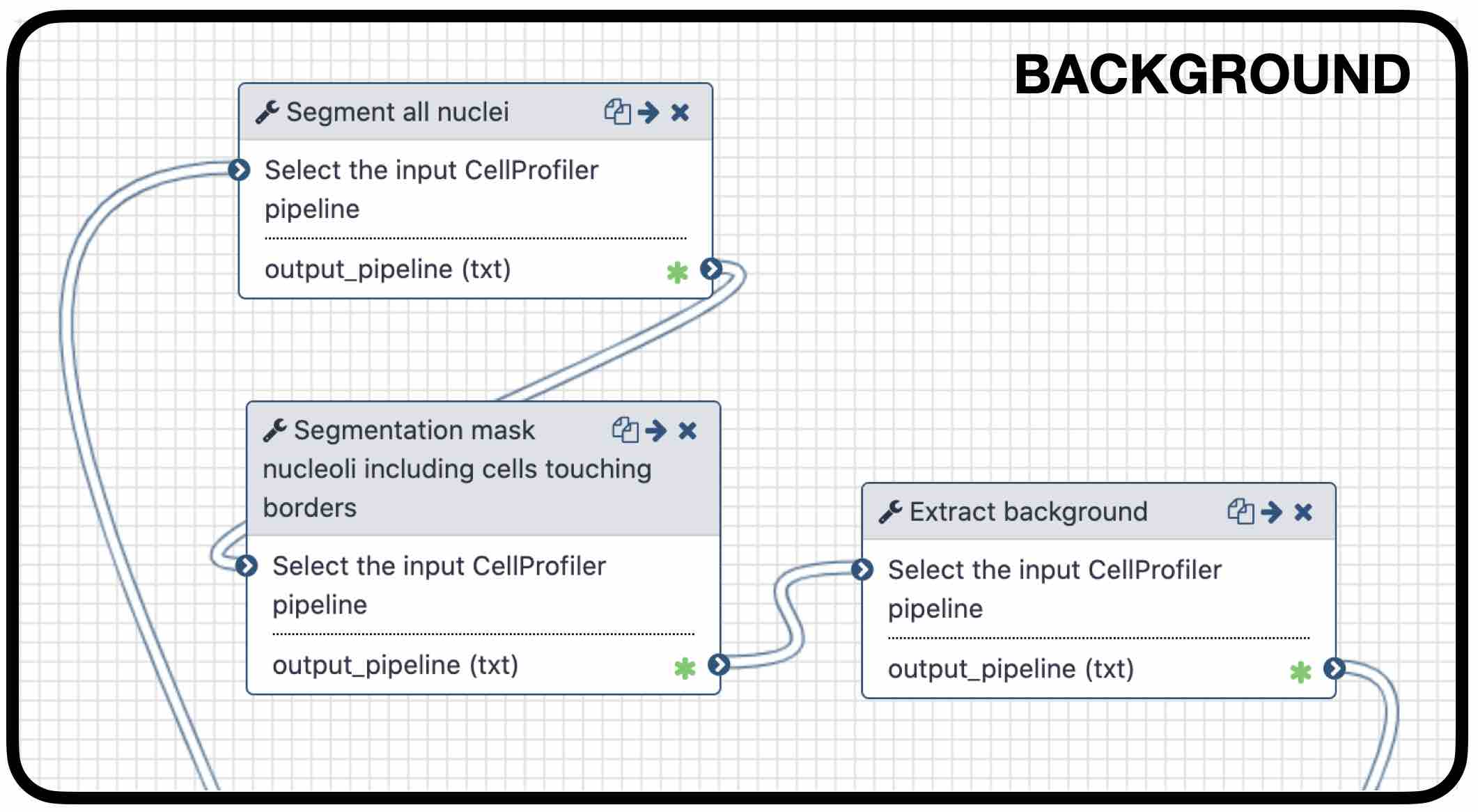
Speaker Notes
The extraction of the background can be useful to measure features that indicate that the images are artefacts. To get the background we first select the foreground and subtract it from the original image. We have partially detected the foreground in the nuclei segmentation in previous steps. However, that mask only included just those objects within a max and a min pixel size. We also discarded the images touching the borders. Here, we get rid of the constraints and segment all the nuclei.
Feature extraction
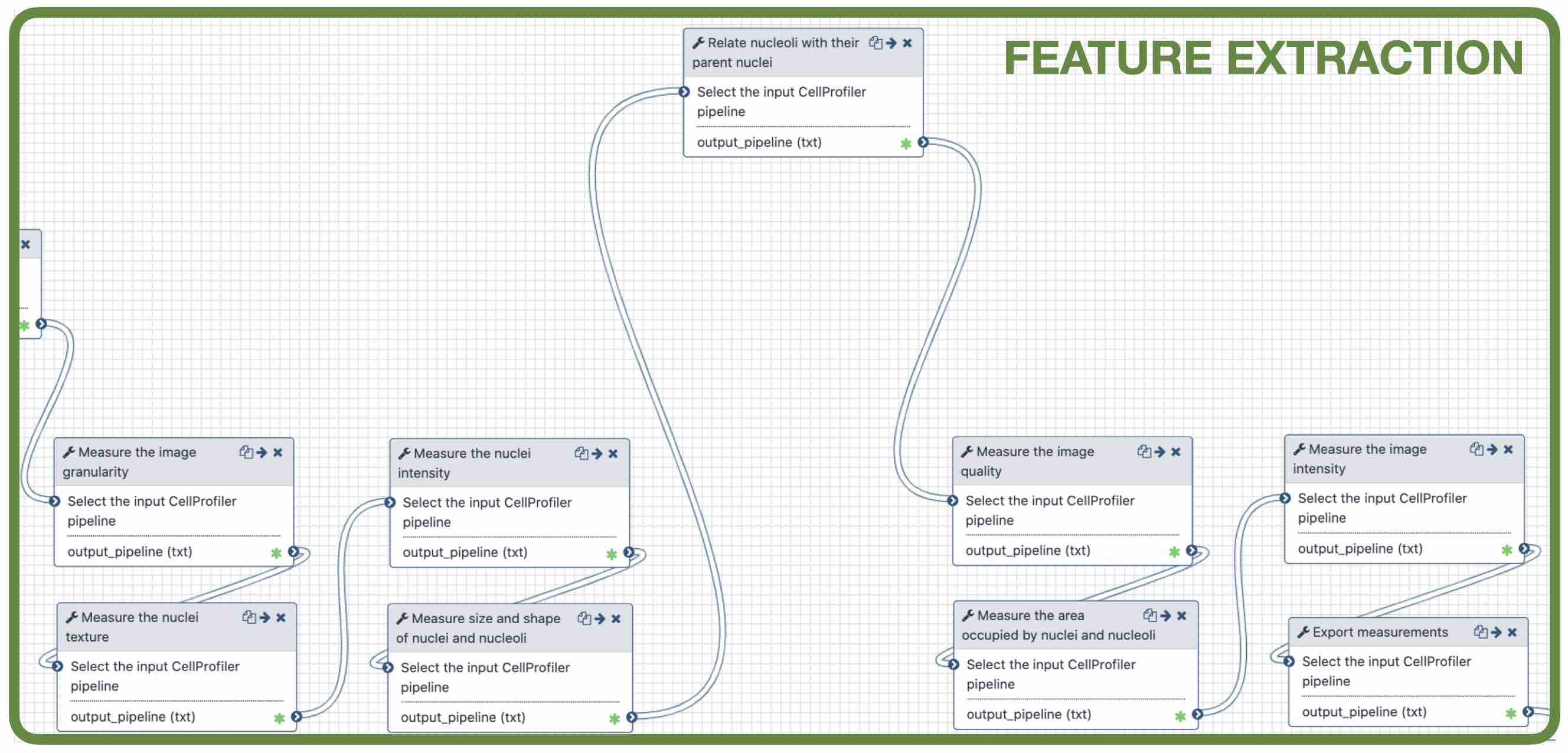
- Important: Relate nucleoli and parent nucleus
Speaker Notes The features can be extracted from the images and the objects. Depending on which type of object and the interest of the study, different parameters can be measured. The module that relates the objects is useful to export a table with the ids of the nucleoli in relation with their parent nuclei. That’s useful for a meaningful interpretation of the data.
Key Points
- Galaxy workflows can download images from the IDR, selecting specific channels, time points, z-stack positions and crop the image in different ways.
- CellProfiler in Galaxy can segment and extract features of any object of interest.
- The features and masks can be exported for further analysis.
Thank you!
This material is the result of a collaborative work. Thanks to the Galaxy Training Network and all the contributors! This material is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This material is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.