Nanopore sequencing
Nanopore sequencing has several properties that make it well-suited for our purposes
- Long-read sequencing technology offers simplified and less ambiguous genome assembly
- Long-read sequencing gives the ability to span repetitive genomic regions
- Long-read sequencing makes it possible to identify large structural variations
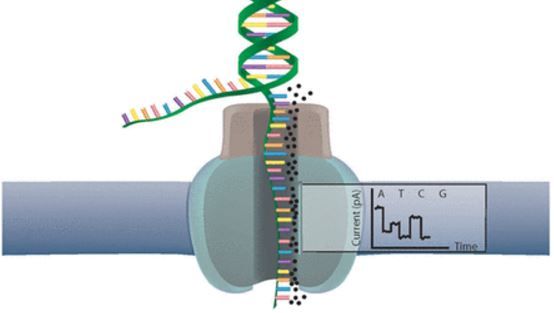
When using Oxford Nanopore Technologies (ONT) sequencing, the change in electrical current is measured over the membrane of a flow cell. When nucleotides pass the pores in the flow cell the current change is translated (basecalled) to nucleotides by a basecaller. A schematic overview is given in the picture above.
When sequencing using a MinIT or MinION Mk1C, the basecalling software is present on the devices. With basecalling the electrical signals are translated to bases (A,T,G,C) with a quality score per base. The sequenced DNA strand will be basecalled and this will form one read. Multiple reads will be stored in a fastq file.
Still have questions?
Gitter Chat Support
Galaxy Help Forum
Want to embed this snippet (FAQ) in your GTN Tutorial?
{% snippet faqs/galaxy/sequencing_nanopore.md %}
