name: inverse layout: true class: center, middle, inverse <div class="my-header"><span> <a href="/training-material/topics/metabolomics" title="Return to topic page" ><i class="fa fa-level-up" aria-hidden="true"></i></a> <a class="nav-link" href="https://github.com/galaxyproject/training-material/edit/main/topics/metabolomics/slides/introduction.html"><i class="fa fa-pencil" aria-hidden="true"></i></a> </span></div> <div class="my-footer"><span> <img src="/training-material/assets/images/GTN-60px.png" alt="Galaxy Training Network" style="height: 40px;"/> </span></div> --- <img src="/training-material/assets/images/GTN.png" alt="Galaxy Training Network" class="cover-logo"/> # Introduction to Metabolomics <div markdown="0"> <div class="contributors-line"> Authors: <a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/lecorguille/" class="contributor-badge contributor-lecorguille"><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/lecorguille?s=27" alt="Avatar">Gildas Le Corguillé</a> <a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/cecilecanlet/" class="contributor-badge contributor-cecilecanlet"><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/cecilecanlet?s=27" alt="Avatar">Cécile Canlet</a> </div> </div> <!-- modified date --> <div class="footnote" style="bottom: 8em;"><i class="far fa-calendar" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="visually-hidden">last_modification</span> Updated: Jul 26, 2021</div> <!-- other slide formats (video and plain-text) --> <div class="footnote" style="bottom: 6em;"> <i class="fas fa-file-alt" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="visually-hidden">text-document</span><a href="slides-plain.html"> Plain-text slides</a> </div> <!-- usage tips --> <div class="footnote" style="bottom: 2em;"> <strong>Tip: </strong>press <kbd>P</kbd> to view the presenter notes | <i class="fa fa-arrows" aria-hidden="true"></i><span class="visually-hidden">arrow-keys</span> Use arrow keys to move between slides </div> ??? Presenter notes contain extra information which might be useful if you intend to use these slides for teaching. Press `P` again to switch presenter notes off Press `C` to create a new window where the same presentation will be displayed. This window is linked to the main window. Changing slides on one will cause the slide to change on the other. Useful when presenting. --- ## Requirements Before diving into this slide deck, we recommend you to have a look at: - [Introduction to Galaxy Analyses](/training-material/topics/introduction) --- # Metabolomics .pull-left[] .pull-right[] «Quantitative measurement of the dynamic multiparametric metabolic response of living systems to pathophysiological stimuli or genetic modification » (Nicholson, 1999) --- ## Definitions - Metabolomics - Newly emerging field of 'omics' research - Comprehensive and simultaneous systematic determination of metabolite levels in the metabolome and their changes over time as a consequence of stimuli - Metabolome - Refers to the complete set of small-molecule metabolites - Dynamic - Metabolites - Intermediates and products of metabolism - Examples include antibiotics, pigments, carbohydrates, fatty acids and amino acids - Primary and secondary metabolites --- ## Definitions .pull-left[ Metabolo **_l_** omics .left[ Metabolic 'fingerprints' (unique for each type of cell or tissue) based on comprehensive quantification i.e. comprehensive and simultaneous systematic determination of metabolite levels in a biological system (cell, tissue, fluid) ]] .pull-right[ Metabolo **_n_** omics .left[ Description of metabolic changes i.e. detection of disrupted metabolic pathways ]] --- ## Metabolomics : the world of small molecules .pull-left[ **Physico-chemical diversity** - Comparison with - DNA/RNA: 4 bases - Proteins: 20 amino acids - Common physico-chemical properties - Extraction/Analysis: easy automation - Metabolites - Number ≥ 150 000 in Nature; most not identified - Wide diversity of structures, functional groups, physico-chemical properties - e.g. lipids, sugars, amino acids, etc. - High turn-over rates (<sec) - Range from 1 pM to 100 mM ] .pull-right[ **Molecular mass range**  <small>80% of metabolites with mol. mass ≤ 600 (E. coli, S. cerevisiae)</small> ] --- ## Analytical challenge  --- ## Complementary analytical tools ### For metabolome investigation 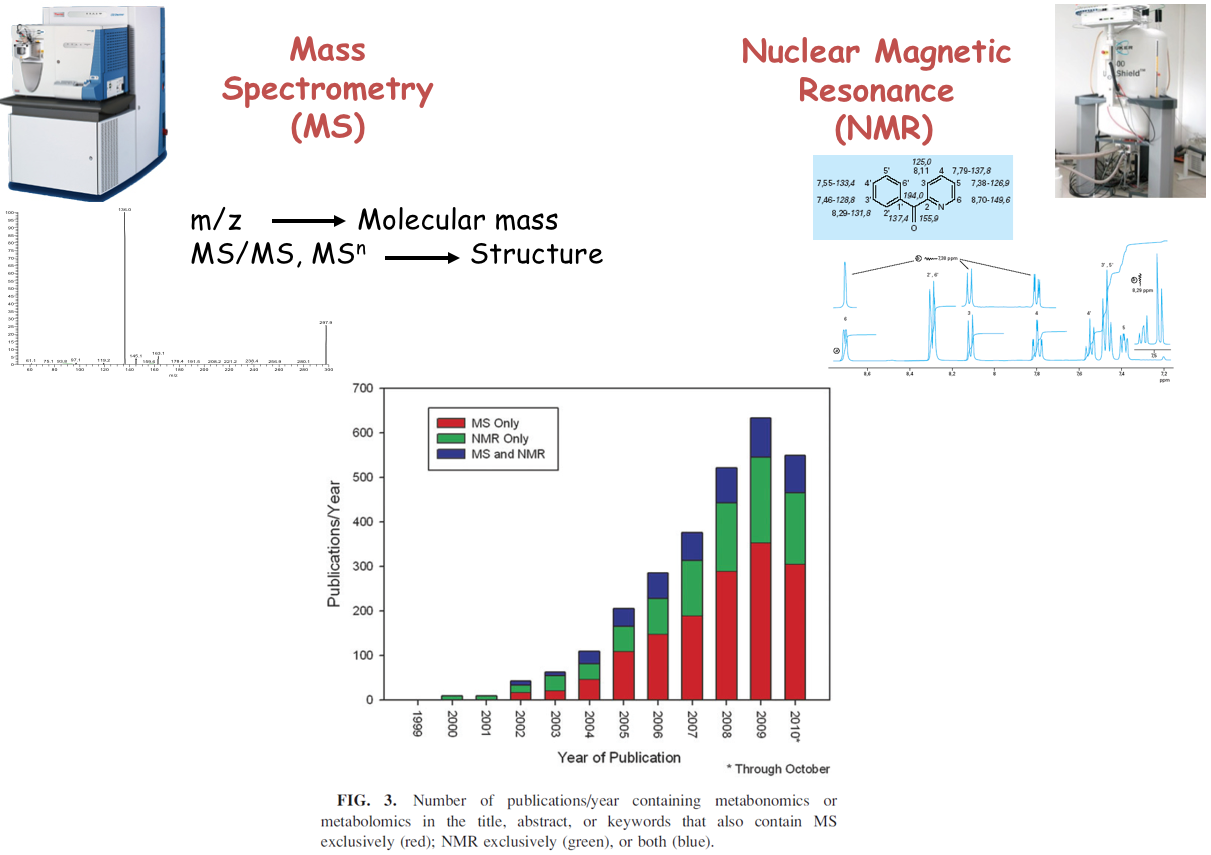 --- ## Strategy: untargeted metabolomics or metabolic fingerprinting 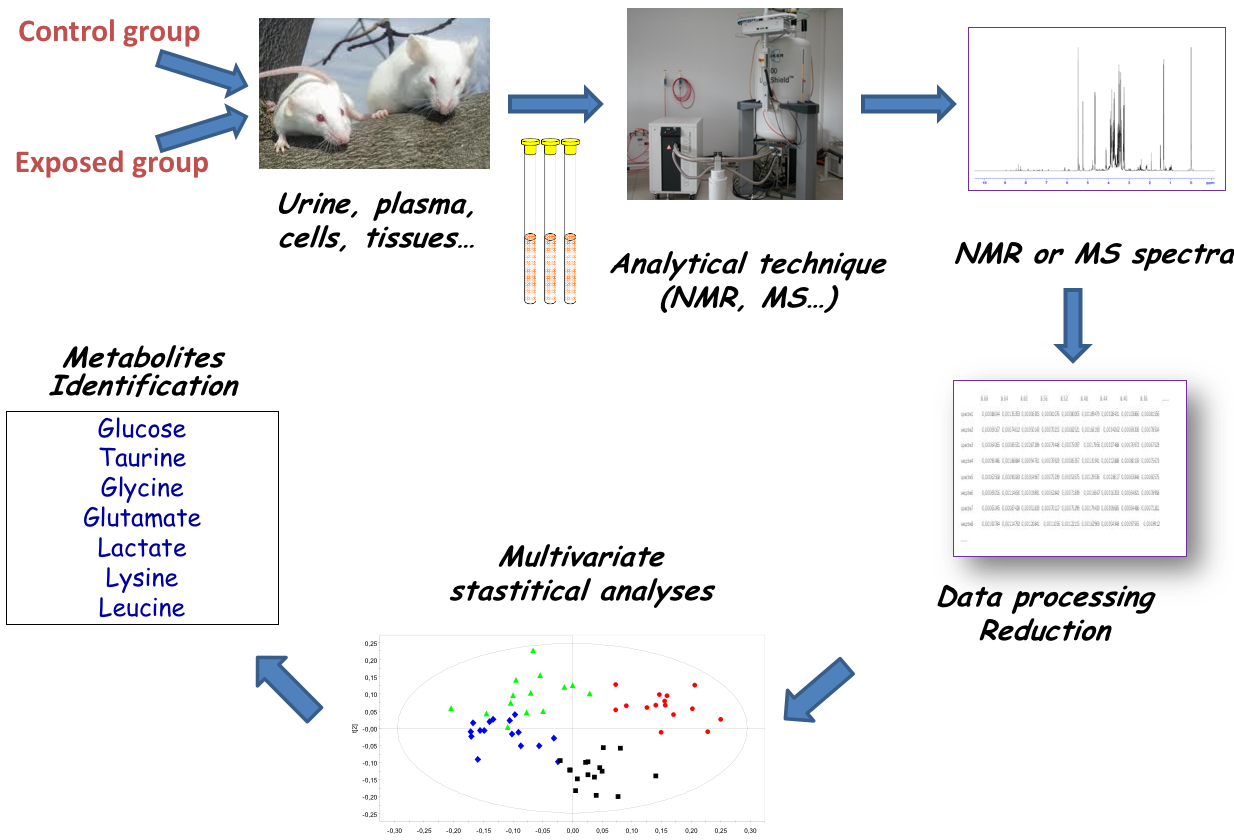 --- ## Strategy: targeted metabolomics Qualitative and quantitative analysis 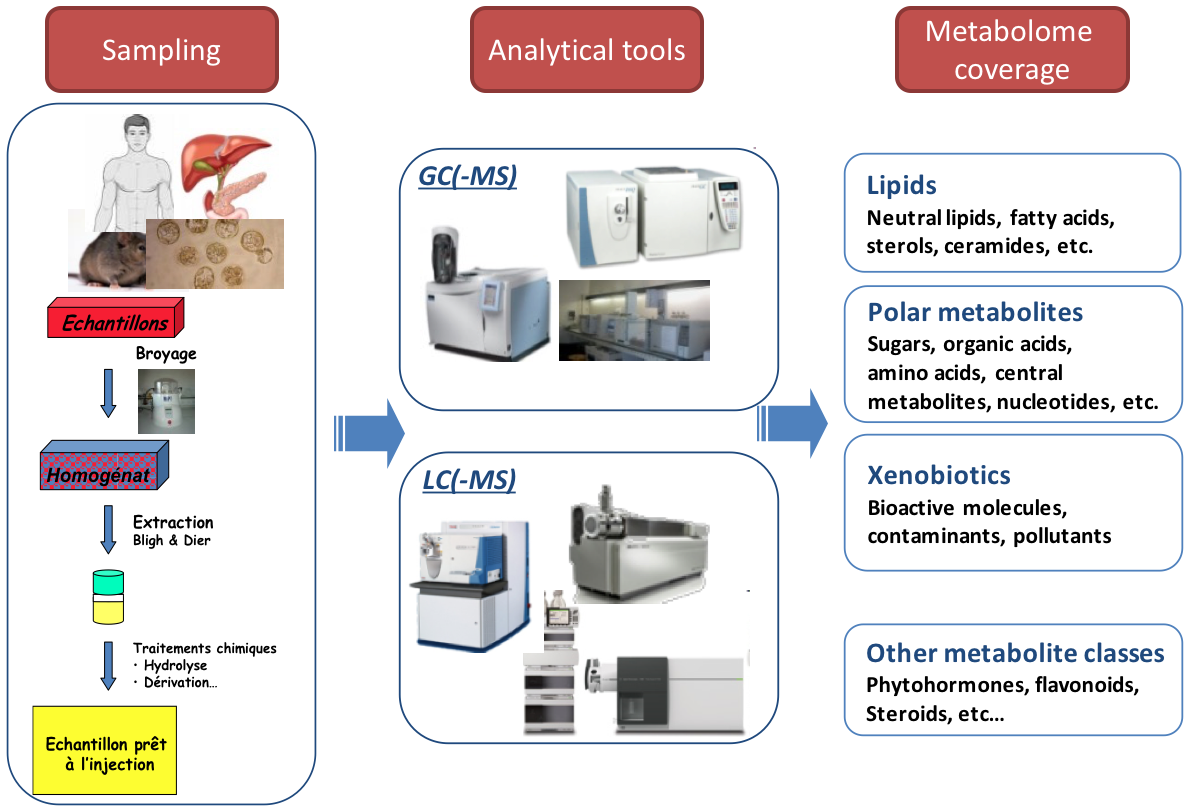 --- ## Related tutorials --- ## Thank You! This material is the result of a collaborative work. Thanks to the [Galaxy Training Network](https://training.galaxyproject.org) and all the contributors! <div markdown="0"> <div class="contributors-line"> Authors: <a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/lecorguille/" class="contributor-badge contributor-lecorguille"><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/lecorguille?s=27" alt="Avatar">Gildas Le Corguillé</a> <a href="/training-material/hall-of-fame/cecilecanlet/" class="contributor-badge contributor-cecilecanlet"><img src="https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/cecilecanlet?s=27" alt="Avatar">Cécile Canlet</a> </div> </div> <div style="display: flex;flex-direction: row;align-items: center;justify-content: center;"> <img src="/training-material/assets/images/GTN.png" alt="Galaxy Training Network" style="height: 100px;"/> </div> <a rel="license" href="https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/"> This material is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License</a>.